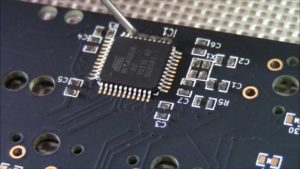
Crack MCU ATTINY24V Program
Crack MCU ATTINY24V and disable the protective memory securify fuse bit, dump the embedded Program out from the flash and eeprom, copy the firmware to blank Microcontroller ATTINY24V which will provide the same functions;
Crack MCU ATTINY24V and disable the protective memory securify fuse bit, dump the embedded Program out from the flash and eeprom, copy the firmware to blank Microcontroller ATTINY24V which will provide the same functions
The ATTINY24V instruction set is highly orthogonal and is comprised of three basic categories.
· Byte-oriented operations
· Bit-oriented operations
· Literal and control operations
Each PIC16 instruction is a 12-bit word divided into an opcode, which specifies the instruction type and one or more operands which further specify the operation of the instruction.
The formats for each of the categories is presented in Figure 10-1, while the various opcode fields are summarized in Table 10-1. For byte-oriented instructions, ‘f’ represents a file register designator and ‘d’ represents a destination designator. The file register designator specifies which file register is to be used by the instruction after unlock microchip pic24fj256gb206.
The destination designator specifies where the result of the operation is to be placed. If ‘d’ is ‘0’, the result is placed in the W register. If ‘d’ is ‘1’, the result is placed in the file register specified in the instruction.
For bit-oriented instructions, ‘b’ represents a bit field designator which selects the number of the bit affected by the operation, while ‘f’ represents the number of the file in which the bit is located.
For literal and control operations, ‘k’ represents an 8 or 9-bit constant or literal value before discover chip renesas m30835fjgp.
All instructions are executed within a single instruction cycle, unless a conditional test is true or the program counter is changed as a result of an instruction. In this case, the execution takes two instruction cycles.
One instruction cycle consists of four oscillator periods. Thus, for an oscillator frequency of 4 MHz, the normal instruction execution time is 1 ìs. If a conditional test is true or the program counter is changed as a result of an instruction, the instruction execution time is 2.
Figure 10-1 shows the three general formats that the instructions can have. All examples in the figure use the following format to represent a hexadecimal number: 0xhhh where ‘h’ signifies a hexadecimal digit.
Tags: crack mcu embedded archive,crack mcu embedded binary,crack mcu embedded code,crack mcu embedded content,crack mcu embedded data,crack mcu embedded eeprom,crack mcu embedded file,crack mcu embedded firmware,crack mcu embedded heximal,crack mcu embedded information,crack mcu embedded memory,crack mcu embedded program