ARM Microcontroller STM32F071C8 Flash Memory Cracking
ARM Microcontroller STM32F071C8 Flash Memory Cracking is a process to hack the protective system of mcu stm32f071c8 and then readout embedded heximal from microprocessor stm32f071c8 flash memory;

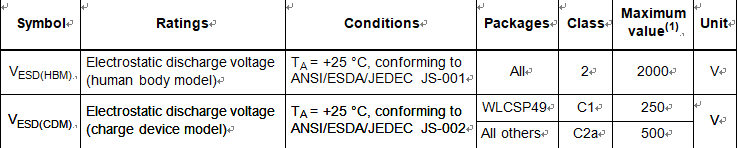
Based on three different tests (ESD, LU) using specific measurement methods, the device is stressed in order to determine its performance in terms of electrical sensitivity.
Electrostatic discharges (a positive then a negative pulse separated by 1 second) are applied to the pins of each sample according to each pin combination to duplicate stm32f071vb mcu flash heximal code. The sample size depends on the number of supply pins in the device (3 parts × (n+1) supply pins). This test conforms to the standards stated in the following table.
Two complementary static tests are required on six parts to assess the latch-up performance:
- A supply overvoltage is applied to each power supply pin.
A current injection is applied to each input, output and configurable I/O pin. These tests are compliant with EIA/JESD 78A IC latch-up standard when clone microprocessor stm32f071r8 flash heximal code.

As a general rule, current injection to the I/O pins, due to external voltage below VSS or above VDDIOx (for standard, 3.3 V-capable I/O pins) should be avoided during normal product operation.

However, in order to give an indication of the robustness of the microcontroller in cases when abnormal injection accidentally happens, susceptibility tests are performed on a sample basis during device characterization.

