Unlock IC ATmega8535 Code
Unlock IC ATmega8535 Code out from its memory, the program from flash and data from eeprom, then copy the firmware to other blank ATmega8535 microcontroller, through Microcontroller reverse engineering can help engineer to find out the scheme of MCU internal structure;
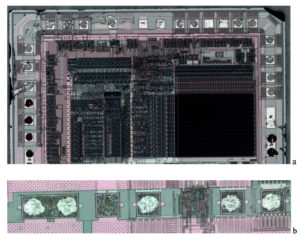
Unlock IC ATmega8535 Code out from its memory, the program from flash and data from eeprom, then copy the firmware to other blank ATmega8535 microcontroller, through Microcontroller reverse engineering can help engineer to find out the scheme of MCU internal structure
The AVR core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers. All 32 registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two independent registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle.
The resulting architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster than conventional CISC microcontrollers. The ATmega8535 provides the following features: 8K bytes of In-System Programmable Flash with Read-While-Write capabilities, 512 bytes EEPROM, 512 bytes SRAM, 32 general purpose I/O lines, 32 general purpose working registers, three flexible Timer/Counters with compare modes, internal and external interrupts, a serial programmable USART, a byte oriented Two-wire Serial Interface, an 8-channel, 10-bit ADC with optional differential input stage with programmable gain in TQFP package, a programmable Watchdog Timer with Internal Oscillator, an SPI serial port, and six software selectable power saving modes if Unlock microcontroller ATmega162 code unlocking.
The Idle mode stops the CPU while allowing the SRAM, Timer/Counters, SPI port, and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power-down mode saves the register contents but freezes the Oscillator, disabling all other chip functions until the next interrupt or Hardware Reset.
In Power-save mode, the asynchronous timer continues to run, allowing the user to maintain a timer base while the rest of the device is sleeping. The ADC Noise Reduction mode stops the CPU and all I/O modules except asynchronous timer and ADC, to minimize switching noise during ADC conversions.
In Standby mode, the crystal/resonator Oscillator is running while the rest of the device is sleeping. This allows very fast start-up combined with low-power consumption. In Extended Standby mode, both the main Oscillator and the asynchro- nous timer continue to run.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high density nonvolatile memory technology. The On-chip ISP Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed In-System through an SPI serial interface, by a conventional nonvolatile memory programmer, or by an On-chip Boot program running on the AVR core.
The boot program can use any interface to download the application program in the Application Flash memory. Software in the Boot Flash section will continue to run while the Application Flash section is updated, providing true Read-While-Write operation.
By combining an 8-bit RISC CPU with In-System Self-Programmable Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel ATmega8535 is a powerful microcontroller that provides a highly flexible and cost effective solution to many embedded control applications.
The ATmega8535 AVR is supported with a full suite of program and system development tools including: C compilers, macro assemblers, program debugger/simulators, In-Circuit Emulators, and evaluation kits.
Tags: ic dump archive unlocking,ic dump code unlocking,ic dump content unlocking,ic dump data unlocking,ic dump eeprom unlocking,ic dump file unlocking,ic dump firmware unlocking,ic dump information unlocking,ic dump memory unlocking,ic dump program unlocking

