Crack MCU ATmega8515L Firmware
Crack MCU ATmega8515L embedded memory and reset the status of microcontroller ATmega8515L from locked to unlocked, Firmware can be dump directly from its flash and eeprom memory by using universal programmer for MCU code recovery;
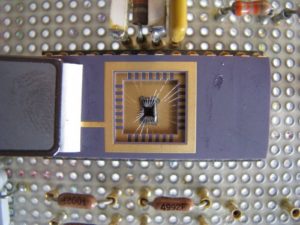
Crack MCU ATmega8515L embedded memory and reset the status of microcontroller ATmega8515L from locked to unlocked, Firmware can be dump directly from its flash and eeprom memory by using universal programmer
To solve this problem, an ATmega8515L compatibility mode can be selected by programming the S8515C Fuse. ATmega8515 is 100% pin compatible with ATmega8515L, and can replace the ATmega8515L on current printed circuit boards. However, the location of Fuse bits and the electrical characteristics differs between the two devices.
Programming the S8515C Fuse will change the following functionality: The timed sequence for changing the Watchdog Time-out period is disabled. See “Timed Sequences for Changing the Configuration of the Watchdog Timer” on page 53 for details.
The double buffering of the USART Receive Registers is disabled. See “AVR USART vs. AVR UART – Compatibility” on page 137 for details. PORTE(2:1) will be set as output, and PORTE0 will be set as input. Port A is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port A output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability when Cracking MCU ATmega32 Code.
When pins PA0 to PA7 are used as inputs and are externally pulled low, they will source current if the internal pull-up resistors are activated. The Port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running. Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability.
As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running. Port C is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port C output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability.
As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port C pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running. Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port D output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability before Crack Mcu.
As inputs, Port D pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running. Port E is an 3-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit).
The Port E output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability. As inputs, Port E pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port E pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running.
Tags: mcu source archive cracking,mcu source code cracking,mcu source content cracking,mcu source data cracking,mcu source eeprom cracking,mcu source file cracking,mcu source firmware cracking,mcu source information cracking,mcu source memory cracking,mcu source program cracking


